Guides and Tutorials
Network Management Guides
How to Efficiently Manage and Maintain a Network of WordPress Sites?
Recommendations:
1. Recommended plugins or tools for network management.
2. Strategies for keeping all sites updated and secure.
3. Tips for handling backups and site migrations.
4. Any workflow suggestions to streamline content updates across the network.

Discover top strategies for network optimization including traffic assessment, QoS policies, hardware upgrades, and regular maintenance to enhance bandwidth and performance.
Optimizing your network is crucial for efficient data transfer, reduced latency, and improved overall performance. Here are the key tips to boost your network's bandwidth:
1. Assess and Monitor Network Traffic - Identify bottlenecks and prioritize critical applications by implementing network monitoring solutions.
2. Update Router Firmware and Optimize Settings - Ensure your router is running the latest firmware and optimize settings like Wi-Fi channel, QoS, guest network, and device connections.
3. Implement Quality of Service (QoS) Policies - Prioritize critical applications to ensure they receive necessary resources and bandwidth.
4. Leverage Load Balancing Techniques - Distribute traffic across multiple servers to improve availability, scalability, and performance.
5. Upgrade to High-Performance Hardware - Invest in faster hardware like 10 Gigabit Ethernet for enhanced speed, reliability, and security.
6. Reduce Network Congestion with Traffic Shaping - Regulate network traffic and prioritize critical applications using traffic shaping techniques.
7. Utilize Data Compression Methods - Reduce data size for faster transmission and improved resource utilization.
8. Segment the Network to Improve Performance - Divide the network into smaller segments to reduce congestion, improve security, and simplify management.
9. Implement Network Caching Solutions - Store frequently accessed files locally to reduce bandwidth usage and improve network connectivity.
10. Regular Network Maintenance and Upgrades - Monitor performance, identify issues, and regularly update hardware and software to ensure optimal network performance.
By following these tips, you can effectively manage network resources, reduce latency, and improve overall bandwidth utilization, ensuring a seamless and efficient network experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Your Queries Answered

Related video from YouTube
1. Assess and Monitor Network Traffic
To optimize network performance and boost bandwidth, you need to understand your network traffic patterns. This involves identifying bottlenecks, detecting anomalies, and making data-driven decisions to enhance performance.
To assess and monitor network traffic effectively, follow these steps:
Steps:
| 1. Choose the right data source |
| 2. Identify key network applications |
| 3. Implement network monitoring solutions |
By following these steps, you’ll be able to establish a robust network monitoring system that helps you stay on top of network performance and make informed decisions to optimize bandwidth.
For the Descriptions of these Steps, Go to https://daily.dev/?r=0
2. Update Router Firmware and Optimize Settings
Updating your router's firmware and optimizing its settings can significantly improve your network's bandwidth.
Here's how to do it:
Update Router Firmware
Outdated firmware can cause performance issues, security vulnerabilities, and compatibility problems. To update your router's firmware:
1. Check the manufacturer's website: Visit your router manufacturer's website to check for firmware updates.
2. Download the update file: Download the latest firmware update file for your router model.
3. Log in to the router: Access your router's web interface using its IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
4. Upload the update file: Upload the downloaded firmware update file to the router.
5. Reboot the router: Restart the router to complete the update process.
Optimize Router Settings
Optimizing your router’s settings can also improve network performance. Here are some tips:
Setting:
| Set up a guest network |
| Limit device connections |
| Change the Wi-Fi channel |
| Enable Quality of Service (QoS) |
Description:
| Segregate guest traffic to prevent bandwidth hogging and security risks. |
| Restrict the number of devices connected to your network to prevent bandwidth overload. |
| Switch to a less congested Wi-Fi channel to reduce interference. |
| Prioritize traffic for critical applications like video conferencing or online gaming. |
By following these steps, you can ensure your router is running with the latest firmware and optimized settings, resulting in improved network performance and increased bandwidth.
3. Implement Quality of Service (QoS) Policies
Implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies is crucial for network optimization. QoS policies allow network administrators to prioritize specific types of traffic, ensuring critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and resources.
Benefits of QoS Policies
QoS policies offer several benefits:
Benefit:
| Better resource allocation |
| Enhanced user experience |
| Improved application performance |
Description:
| Prioritize critical applications to reduce latency and improve performance. |
| Minimize disruptions and delays to increase user productivity and satisfaction. |
| Allocate resources efficiently to reduce congestion and improve overall network performance. |
How to Implement QoS Policies
To implement QoS policies, follow these steps:
1. Identify critical applications: Determine which applications require priority treatment and allocate resources accordingly.
2. Classify traffic: Classify traffic into different categories based on priority, ensuring critical applications receive the necessary resources.
3. Configure QoS settings: Configure QoS settings on network devices, such as routers and switches, to prioritize traffic accordingly.
4. Monitor and adjust: Continuously monitor network performance and adjust QoS policies as needed to ensure optimal performance.
By implementing QoS policies, network administrators can ensure critical applications receive the necessary resources, resulting in improved performance and a better user experience.
4. Leverage Load Balancing Techniques
Load balancing is a crucial technique for network optimization, ensuring that no single server becomes overwhelmed with requests. By distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, load balancing improves application availability, scalability, and performance.
Load Balancing Benefits
Load balancing offers several benefits:
Benefit:
| Improved Availability |
| Enhanced Scalability |
| Better Performance |
| Increased Security |
Description:
| Distribute traffic across multiple servers to minimize downtime. |
| Easily add or remove servers as needed to handle changes in traffic volume. |
| Reduce server response times and improve overall application performance. |
| Protect against (DoS) and (DDoS) attacks by distributing traffic across multiple servers. |
Load Balancing Algorithms
There are several load balancing algorithms to choose from:
Algorithm:
| Round Robin |
| Source IP Hash |
| Least Connections |
| Weighted Least Connections |
Description:
| Distribute traffic evenly across all servers in a sequence. |
| Use the client’s IP address to determine which server to direct traffic to. |
| Direct traffic to the server with the fewest active connections. |
| Assign weights to servers based on their capacity and direct traffic accordingly. |
By leveraging load balancing techniques, network administrators can ensure that their applications are always available, scalable, and performing at their best.
5. Upgrade to High-Performance Hardware
Upgrading your network hardware can significantly improve performance. With the increasing demands of modern business applications, traditional Gigabit Ethernet networks are struggling to keep up. This is where 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) comes in, offering a tenfold increase in speed and performance.
Why 10 GbE?
Here are some benefits of upgrading to 10 GbE:
Benefit:
| Faster Backbone |
| Enhanced Security |
| Unparalleled Speed |
| Improved Server Capabilities |
Description:
| Create a fast and reliable network backbone, ensuring consistent performance and minimal downtime. |
| Enjoy enhanced security with 10 GbE, which offers a wired solution resistant to external interference, etc. |
| Experience unparalleled speed with 10 GbE, ideal for applications that require high-bandwidth, etc. |
| Upgrade your server capabilities, allowing for more efficient data transfer and storage. |
By upgrading to high-performance hardware like 10 GbE, you can significantly improve your network’s performance, reliability, and security, ensuring that your business applications run smoothly and efficiently.
Network Troubleshooting Steps:
To implement QoS policies, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Problem.
2. Establish a Theory of Probable Cause.
3. Test Probable Cause Theory to Determine Actual Cause.
4. Establish an Action Plan and Execute the Plan.
5. Verify Full System Functionality.
6. Document the Process.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Definition, Benefits, Types, and Trends!
Cloud computing touches us all. There’s an explosion of cloud-based applications and services.

Hareem Ejaz
Cloud computing is defined as the use of hosted services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software over the internet. Since cloud computing began, the world has witnessed an explosion of cloud-based applications and services in IT, which continue to expand. Almost every application we use resides on the cloud, helping us save storage space, expenses, and time. This article discusses the types of cloud computing and 10 trends to watch out for.
Table of Contents
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the use of hosted services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software over the internet. The data is stored on physical servers, which are maintained by a cloud service provider. Computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, are available on-demand, without direct management by the user in cloud computing.
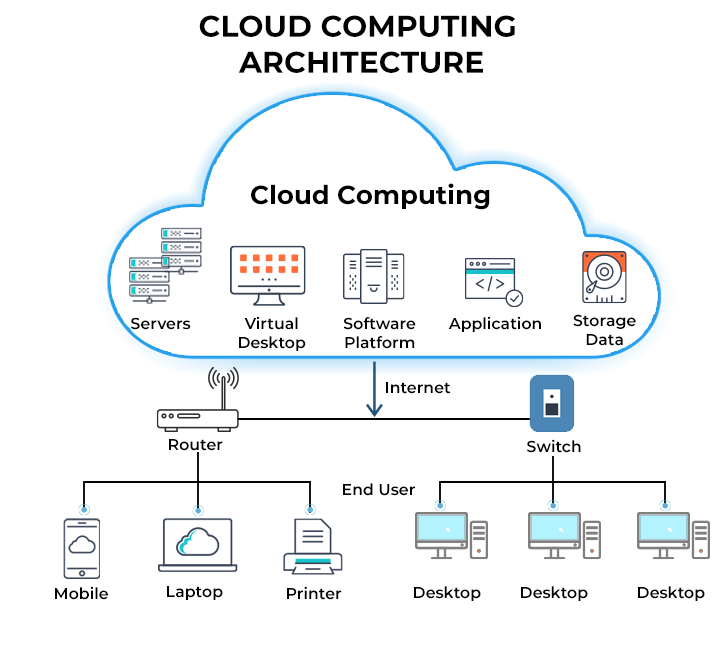
Cloud Computing Architecture
Instead of storing files on a storage device or hard drive, a user can save them on cloud, making it possible to access the files from anywhere, as long as they have access to the web. The services hosted on cloud can be broadly divided into infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). Based on the deployment model, cloud can also be classified as public, private, and hybrid cloud.
Further, cloud can be divided into two different layers, namely, front-end and back-end. The layer with which users interact is called the front-end layer. This layer enables a user to access the data that has been stored in cloud through cloud computing software.
The layer made up of software and hardware, i.e., the computers, servers, central servers, and databases, is the back-end layer. This layer is the primary component of cloud and is entirely responsible for storing information securely. To ensure seamless connectivity between devices linked via cloud computing, the central servers use a software called middleware that acts as a bridge between the database and applications.
What Is IoT Integration?
Internet of Things is a concept where everyday objects like refrigerators, cars, or even your light bulbs can connect to the internet and communicate with each other and with us. IoT enables your refrigerator to send you a message letting you know when you’re low on milk, or your light bulbs to turn themselves off when they sense you’ve left the room.
IoT integration is about getting all these different devices to work together in a coordinated way like a team sport. Each individual player (or in this case, device) is good at something different, but they need to work together to achieve a common goal.
For example, when you’re going to bed, you could manually turn off all the lights, check the doors are locked, adjust the thermostat, and so on. But with IoT integration, you might just tell your smart speaker “Goodnight,” and it will communicate with all the other connected devices in your house to make sure everything is set for the night – lights off, doors locked, and temperature adjusted.

Doing this requires some behind-the-scenes work, like setting up the devices to connect to your home network and making sure they can “talk” to each other in a language they all understand. It can also involve setting up rules or “routines” (like the “Goodnight” command) so that the devices know what to do in different situations.
Basically, IoT integration is about getting all of your internet-connected devices to work together smoothly and efficiently, to make your life easier and more convenient.
What Is an SD-WAN?
A wide area network (WAN) is a network that connects local area networks (LANs) across long distances. Large organizations often use a WAN to connect their various branch offices and locations to the central corporate network. In traditional WANs, the software that defines how traffic flows in the network is tightly integrated with the hardware that actually directs the traffic. Typically this software/hardware combination is purchased from a single networking vendor.
A software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) is a more flexible WAN architecture that can take advantage of multiple hardware platforms and connectivity options. The controlling software works with any networking hardware. An organization can set up an SD-WAN using off-the-shelf hardware rather than specialized hardware. This makes SD-WANs cheaper, more flexible, and more scalable than traditional WANs.
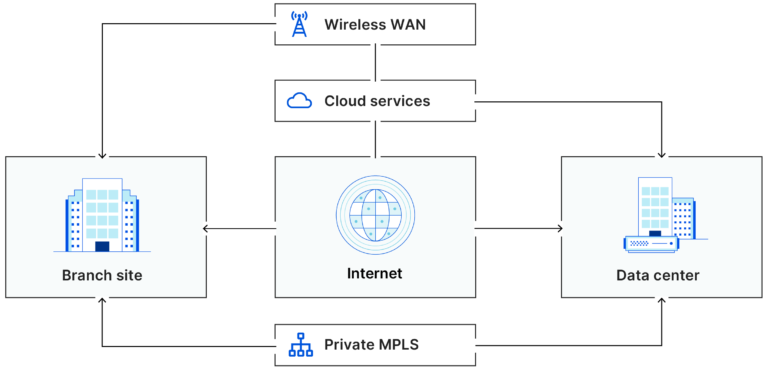
Think about the difference between a desktop computer that runs a proprietary operating system and a desktop computer that runs an operating system that works with a variety of computers, for instance Linux. For the first desktop computer, the software and the hardware are tightly integrated. The operating system and the hardware on which it runs must be purchased together. In contrast, Linux operating systems can run on many types of desktop computers from various vendors. Someone who wants a computer that runs Linux can choose from a wide range of computers, from cheaper models to expensive high-end gaming computers, or they can build their own computer from off-the-shelf hardware components.
While the pros and cons associated with this choice in desktop computers are not related to the pros and cons associated with traditional WANs versus SD-WANs, a similar principle applies: as with Linux operating systems, SD-WAN software is decoupled from the underlying hardware, giving organizations more choices for what hardware they will use.



















